DAuthenticatorHook Documentation¶
Introduction¶
The DAuthenticatorHook is a custom Airflow hook designed to manage account authentication and availability for different tools (HTML or API-based drivers). This hook connects to a PostgreSQL database, allowing the management of cookies, session handling, and account status updates through SQL requests.
It is particularly used to handle:
-
Verifying account availability.
-
Managing cookies and sessions.
-
Triggering login workflows when necessary.
Accounts Availibility¶
Dauthenticator hook, mainly hundel 2 differents type of accounts: The accounts used for html drivers and the accounts used for api drivers
HTML Driver account:¶
The diagram below represents the workflow for verifying account availability when the used_tool used to implement the drive to which the account belongs is "Request" or "Selenium".
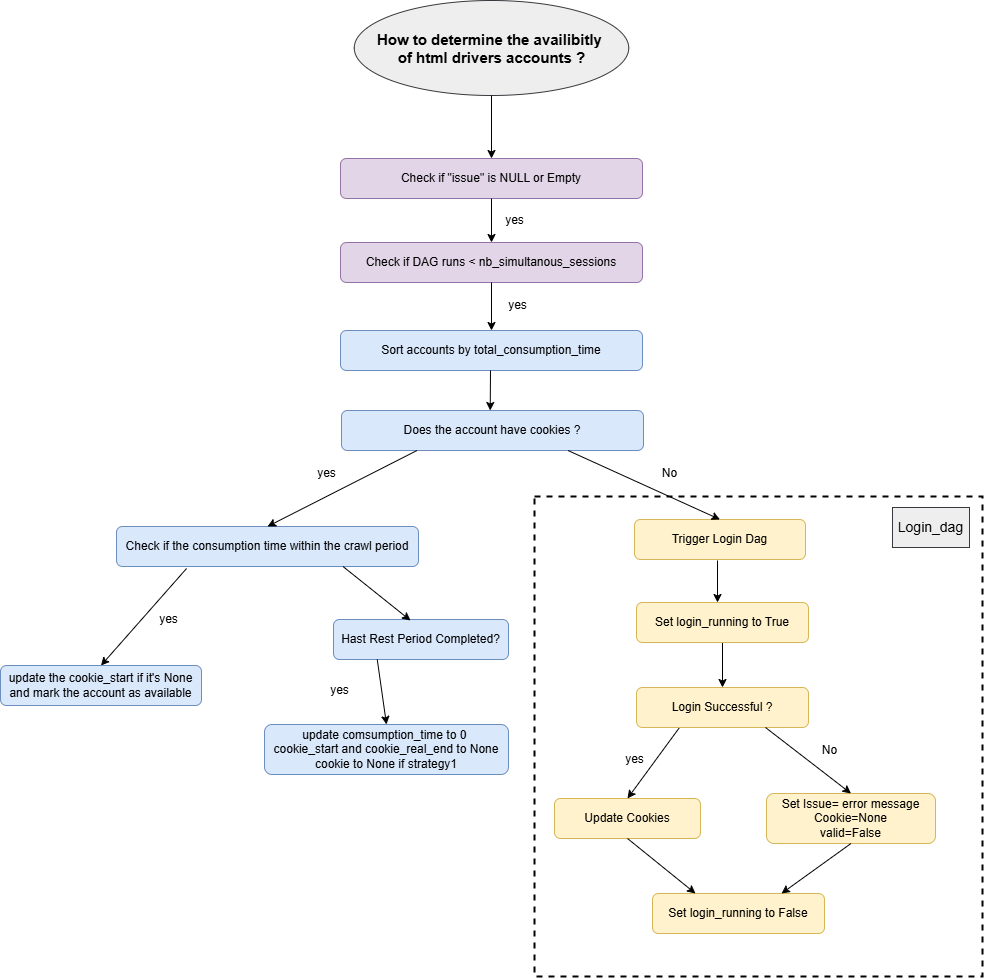
Account Selection Workflow¶
The get_available_accounts function retrieves accounts from the cookies table for the specified driver name. It applies the following constraints:
-
The
issuecolumn must beNULLor empty. -
The number of airflow_dagrun rows associated with the account (
dagrun_count) must be less than the allowed simultaneous sessions (nb_simultanous_sessions).
The retrieved accounts are sorted by their total_consumption_time, prioritizing the least used accounts for crawling.
Join Operations for Additional Information¶
To retrieve relevant information for each account, the function performs the following joins:
-
Cookies and html_driver:
-
The
cookiestable is joined with thehtml_drivertable on thehtml_driver_idcolumn. -
This join fetches driver-related details like
nb_simultanous_sessions,crawl_period_per_hour, andrest_period_per_hour. -
Cookies and airflow_dagrun:
-
A left join is performed with the
airflow_dagruntable using thecookie_id. -
This retrieves the count of active DAG runs (
dagrun_count) associated with each account, helping enforce the session limits.
These joins allow the function to combine account specific data from the cookies table with driver constraints and session tracking information.
Checking Account Cookies¶
If the account has cookies:
-
Check if the
consumption_timeis below the maximum crawl period. -
If true: The account is considered available. Additionally, update the
cookie_startto the current datetime if it was previouslyNULL. -
If false: Verify if the account's rest period is complete.
-
If the rest period is complete: Reset the
consumption_timeto 0 and setcookie_startandcookie_real_endtoNULLand cookie to None if the driver's strategy isstrategy1
If the account does not have cookies:
- The login_dag is triggered using the
run_dagmethod to generate new cookies.
Login Workflow¶
When an account does not have cookies or requires a login, the login_dag is triggered, following this workflow:
- Set the
login_runningflag toTrue:
This ensures that the login process is launched only once for each account.
-
Instanciate the driver and execute login:
-
If login is successful:
-
Generate new cookies and update the
cookiecolumn with the new value. -
If login fails:
-
Update the account's state, setting
validtoFalseand logging the error message in theissuecolumn. -
Regardless of login success or failure, the
login_runningflag is set toFalseto mark the completion of the login attempt.
Methods and Features¶
This section provides an explanation of the main methods implemented in the DAuthenticatorHook and their functionality.
1. Fetching Accounts (get_available_accounts)¶
The get_available_accounts method is responsible for retrieving accounts that are ready for use based on the driver name and the tool type (used_tool).
2. Updating Cookies and Account State¶
Managing the state of accounts and ensure their details are accurately maintained in the database.
- update_cookies_account:
Updates specific fields in the cookies table, including:
-
cookie_start,cookie_real_end: Tracks session start and end times. -
cookie: Stores the cookie values for the account. -
consumption_time: Tracks the consumption time for the account. -
issue: Logs any errors or issues encountered during the account's session. -
update_login_status:
Specifically handles updates after a login attempt.
-
If login is successful: Updates the
cookiefield with the generated value. -
If login fails: Sets
validtoFalseand logs the error message in theissuecolumn.
3. Managing the Login Workflow¶
- set_login_running:
This method sets the login_running flag for an account to True. It prevents multiple simultaneous login attempts for the same account, ensuring the login workflow is processed only once.
- run_dag:
Triggers the login_dag to handle the login process it takes the account details as configuration for the DAG. and the id of dag to lunch
4. Updating Cookies and Consumption Time¶
After each crawl we need to update the new values of the cookies, the consumption_time, the total consumption time and the cooki_real_end date using update_cookies_and_consumption_time
5. DAG Run Mapping¶
The DAG Run Mapping handle the association of accounts with active DAG runs in the airflow_dagrun table.
-
add_dagrun_account_mappings: Adds a record linking an account (from
cookiesorapi_credentials) to a specific DAG run and stores thedag_run_idand session start time. Which allows us to know how many sessions are lunched using each account -
delete_dagrun_account_mappings: Removes the mapping for a specified
dag_run_id, cleaning up the registred sessions once the DAG run is complete.
API Driver account¶
The diagram below represents the workflow for verifying account availability when the driver’s used_tool is "API".

To retrieve available accounts the system uses the get_available_accounts(driver_name, nb_accounts) method. The implementation varies depending on used_tool. Below are the important implementation details (Behavior when used_tool == "API" plus how that ties into other helper methods).
How get_available_accounts works for API drivers¶
-
The service first determines the
used_toolfordriver_nameviaget_media_used_tool(driver_name). -
When
used_tool == "API"the method runs an SQL query that will do: -
Filtering / selection logic:
-
Only credentials whose
issueisNULLandactive = TRUEare considered. -
The query excludes any credential that already has active orchestrator runs (
dagrun_count = 0is required). -
Results are ordered by
quota_consumption ASCso the least-consumed credentials are preferred.
-
-
Post-query handling:
-
The code fetches rows, maps them to dictionaries (
columns+row) and returns up tonb_accounts. -
For API credentials there is no further cookie/rest logic — selection is quota-driven.
-
API quota management (how consumption is updated)¶
-
When an API-driven task consumes quota, the service uses
update_api_quota_consumption(account_id, quota)which:-
Fetches current
quota_consumptionand the driver'srequest_limit_per_day: -
Computes
new_quota_consumption = current_quota + quota. -
If
new_quota_consumption > request_limit_per_day→ the account is deactivated andquota_consumptionreset to0:This enforces per-driver daily request limits and forces operator intervention or a scheduled reset.
-
Otherwise the
quota_consumptionis updated to the new value. -
Changes are committed; on error the transaction is rolled back.
-
-
There are companion helper endpoints / methods:
-
get_api_accounts()— returnsac.id, ac.quota_consumption, ac.api_driver_id, ad.quota_rest_frequency, ad.request_limit_per_dayfor auditing and monitoring. -
activate_account(account_id)— re-activates an account and resetsquota_consumption/ clearsissue:
-